The spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus of a radioactive substance resulting in the emission of radiation from the nucleus is known as Radioactive decay. The nuclide which undergoes decay in a radioactive process is a parent nuclide, and the nuclide which is produced in the radioactive process is a daughter nuclide.
The Radioactive Formula is given by
Where N0 = the initial quantity of the substance and N is the quantity still remained and not yet decayed.
T is the half-life of the decaying quantity
e is the Euler’s number equal to 2.71828
The differential equation of Radioactive Decay Formula is defined as
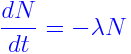
The half-life of an isotope is the time taken by its nucleus to decay to half of its original number. It can be expressed as
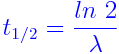
Example 1 – Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5.730 years. Determine the decay rate of Carbon-14.
Solution – If 100 mg of carbon-14 has a half-life of 5.730 years (t=5.730). We can use the formula.
=0.693/5.730
= 0.1209
Comments